

-

Telephone
Hot line
+86-18217040202
-
Phone Call
+86-18217040202
-
Go To Top
Contact Us

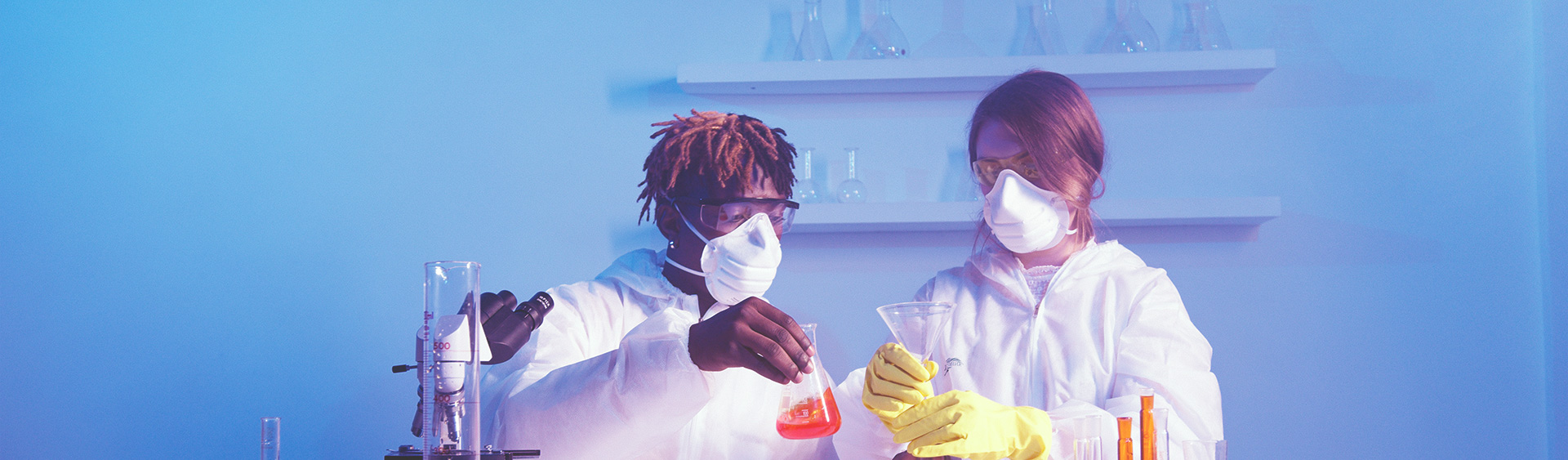
Animal Hyper/Hypobaric Chamber (Dual Functions)
Product model:
ProOx-850Detailed introduction:
Product Description
Animal Hyper/Hypobaric Chamber (Dual Functions) is an experimental oxygen chamber specially designed for experimental animals, which can be used for both low pressure oxygen and hyperbaric oxygen research. With manual and automatic operation modes, it can be used to simulate high-plateau environment and create successful animal disease models such as cerebral edema model and pulmonary hypertension model.
Features
l 10-inch touch screen, easy to operate
lReal-time display of dynamic change curves of pressure and oxygen concentration
l The maximum altitude can be simulated at 10,000 meters, and the maximum pressure can reach 0.15MPa
l With automatic ventilation function, abide with Good Animal Feeding Practice
l The animal chamber is made of imported thickened acrylic, which is strong and durable
l It has a pull-out type animal bedding, which is convenient for putting animals and cleaning
l With a gas buffer, reducing the impact of fine jet stream gas on animals
l Multi-stage air filter ensures clean gas while removing particulate matter, moisture, oil and oil vapor from the air supply
lProvide multi-directional alarm function to remind experimenters of abnormal state
Application field
Altitude sickness research, research on pulmonary edema, cerebral edema, pulmonary hypertension and other diseases
Model Selection
Product Name | Model | Descriptions |
Hypo/Hyperbaric Chamber | ProOx-850 | Can be used for both hypobaric and hyperbaric researches |
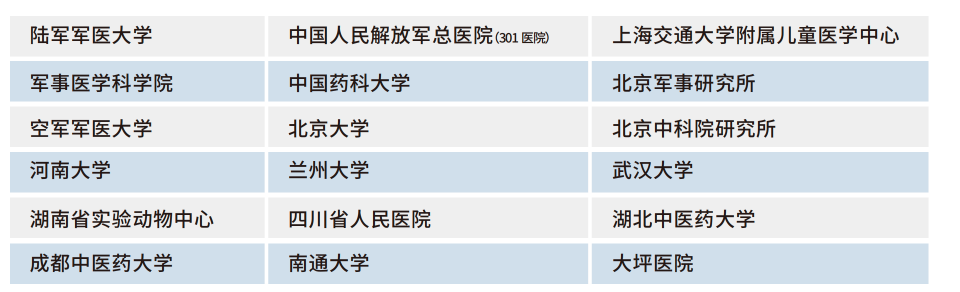
Customer List
1. Army Medical University
2. Academy of Military Medical Sciences
3. Air Force Medical University
4. Henan University
5. Hunan Experimental Animal Center
6. Chengdu University of Chinese Medicine
7. The General Hospital of the People's Liberation Army (301 Hospital
8. China Pharmaceutical University
9. Peking University
10. Lanzhou University
11. Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital
12. Nantong University
13. Shanghai JiaoTong University Children's Medical Center
14. Beijing Military Research Institute
15. Institute of Chinese Academy of Sciences
16. Wuhan University
17. Hubei University of Chinese Medicine
18. Daping Hospital
压等动物模型。
产品特点
· 采用10英寸触摸屏,操作简单
· 实时显示压力和氧气浓度动态变化曲线
· 最高可模拟10000米海拔高度,最大压力达0.15MPa
· 具备自动换气功能,符合动物饲养规范
· 动物舱体采用进口亚克力加厚耗材,坚固可靠
· 具有抽拉式动物载床,方便去放动物与清洁
· 具有气体缓冲器,减小细股急流气体对动物的影响
· 多级空气过滤器确保气体清洁,同时去除空气供应中的微粒物质、水分、油和油蒸汽
· 提供多方位的报警功能,提醒实验人员异常状态
应用领域
高原医学研究、肺水肿、脑水肿、肺动脉高压等疾病研究
型号说明
| 名称 | 型号 | 说明 |
| 动物高低压氧舱 | ProOx-850 | 可同时用于低压氧和高压氧研究 |
使用客户名单
Reference
[1]Ma Jinqiu,Wang Chenyun,Sun Yunbo,Pang Lulu,Zhu Siqing,Liu Yijing,Zhu Lin,Zhang Shouguo,Wang Lin,Du Lina. Comparative study of oral and intranasal puerarin for prevention of brain injury induced by acute high-altitude hypoxia.[J] International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,591
[2]Guijuan Chen,Kang Cheng,Yun Niu,Li Zhu,Xueting Wang.Epicatechin gallate prevents inflammatory response in hypoxia-activated microglia and cerebral edema by inhibiting NF-κB signaling.[J]Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics ,Volume 729, 109393;
[3]Yapeng,LuPanpanChang,WangwangDing,JiangpeiBian,DanWang,XuetingWang,QianqianLuo,XiaomeiWu,LiZhu.Pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial division attenuates simulated high-altitude exposure-induced cerebral edema in mice: Involvement of inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway in glial cells.[J] European Journal of Pharmacology,Volume 929,2022,175137
[4]Jun-Yu Wei, Miao-Yue Hu, Xiu-Qi Chen, Feng-Ying Lei, Jin-Shuang Wei, Jie Chen, Xuan-Kai Qin & Yuan-Han Qin .Rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced renal cell apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway in a PPARγ-dependent manner, [J] European Journal of Pharmacology,Renal Failure, 44:1, 2056-2065
[5]Yilan Wang, Zherui Shen, Caixia Pei, Sijing Zhao, Nan Jia, Demei Huang, Xiaomin Wang, Yongcan Wu, Shihua Shi, Yacong He, Zhenxing Wang,Eleutheroside B ameliorated high altitude pulmonary edema by attenuating ferroptosis and necroptosis through Nrf2-antioxidant response signaling, [J] Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 156, 2022,113982
[6]Fang Zhao, Yan Meng, Yue Wang, Siqi Fan, Yu Liu,Xiangfeng Zhang, Chenyang Ran, Hongxin Wang and Meili Lu,Protective effect of Astragaloside IV on chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction through the calpain-1/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway.[J] Frontiers in Pharmacology,10.3389/fphar.2022.920977
[7]Jing Zhang , Jian-Zhong Jiang , Jun Xu , Chen-Yu Xu , Shan Mao , Ying Shi , Wei Gu , Chun-Fang Zou , Yue-Ming Zhao , Liang Ye.”Identification of Novel Biomarkers for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Promoted by Obstructive Sleep Apnea”[J]Annals of Vascular Surgery, Available online 2 February 2023
[8]Zhang, C., Sun, Y., Guo, Y. et al. “JMJD1C promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation by activating glycolysis in pulmonary arterial hypertension. “[J].Cell Death Discov. 9, 98 (2023).
[9]Zhang, L., Liu, X., Wei, Q. et al. “Arginine attenuates chronic mountain sickness in rats via microRNA-144-5p. “[J]. Mamm Genome 34, 76–89 (2023).
[10]Yanhong Pei a b, Lifei Huang c, Tong Wang c, Qinhan Yao a, Yanrong Sun a, Yan Zhang a, Xiaomei Yang a, Jiliang Zhai d, Lihua Qin a, Jiajia Xue c, Xing Wang c, Hongquan Zhang a b, Junhao Yan."Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells loaded into hydrogel/nanofiber composite scaffolds ameliorate ischemic brain injury. materialstoday ADVANCES, Volume 17, March 2023, 100349.
[11]Ma Jinqiu,Wang Chenyun,Sun Yunbo,Pang Lulu,Zhu Siqing,Liu Yijing,Zhu Lin,Zhang Shouguo,Wang Lin,Du Lina. "Comparative study of oral and intranasal puerarin for prevention of brain injury induced by acute high-altitude hypoxia" . [J] International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,591
[12]Jun-Yu Wei, Miao-Yue Hu, Xiu-Qi Chen, Feng-Ying Lei, Jin-Shuang Wei, Jie Chen, Xuan-Kai Qin & Yuan-Han Qin ."Rosiglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced renal cell apoptosis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway in a PPARγ-dependent manner" . [J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,Renal Failure, 44:1, 2056-2065
[13]Yilan Wang, Zherui Shen, Caixia Pei, Sijing Zhao, Nan Jia, Demei Huang, Xiaomin Wang, Yongcan Wu, Shihua Shi, Yacong He, Zhenxing Wang,"Eleutheroside B ameliorated high altitude pulmonary edema by attenuating ferroptosis and necroptosis through Nrf2-antioxidant response signaling" . [J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Volume 156, 2022,113982
[14]Yanfei Zhang, Jinyu Fang, Yingyue Dong, Huiru Ding, Quancheng Cheng, Huaicun Liu, Guoheng Xu, Weiguang Zhang“High-Altitude Hypoxia Exposure Induces Iron Overload and Ferroptosis in Adipose Tissue.” [J]. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2367.
[15]Wan-ping Yang, Mei-qi Li, Jie Ding, Jia-yan Li, Gang Wu, Bao Liu, Yu-qi Gao, Guo-hua Wang, Qian-qian Luo. "High-altitude hypoxia exposure inhibits erythrophagocytosis by inducing macrophage ferroptosis in the spleen.” [J]. bioRxiv preprint, 2023.03.23.533972
[16]Xueting Wang, Yuqi Xie, Yun Niu, Baolan Wan, Yapeng Lu, Qianqian Luo, Li Zhu.CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signal mediates M1-type microglia and accelerates high-altitude-induced forgetting[J].2023-05-10 ,DOI:10.3389/fncel.2023.1189348
[17]Liu,J,Peng, S,Ye,L, Sun, Y, Zhao, Q, Wei, H, Luo, Q, He M, & Wang, G(2023).“ Neuroinflammation aggravated by traumatic brain injury at high altitude is reversed by L-serine via NFAT1-mediated microglial polarization.”[J]. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 17, 1152392. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1152392
[18]Ru Zhang,Ailin Yang,Lin Zhang,Linjie He,Xiaoming Gu,Caiyong Yu,Zhenxing Lu,Chuang Wang, Feng Zhou,Fei Li,Lele Ji,Jinliang Xing,Haitao Guo."MFN2 deficiency promotes cardiac response to hypobaric hypoxia by reprogramming cardiomyocyte metabolism.”[J]. WILEY Online Library,2023-07-04 DOI: 10.1111/apha.14018